The world is still struggling to adapt to the effects of climate change and the degradation of the environment, and as a result, there has been a rise in interest in environmentally responsible agricultural practices such as organic farming. Even though there is mounting evidence that organic farming is preferable to conventional agriculture from an environmental standpoint, it is essential to have a solid understanding of the particular ways in which organic farming has an impact on the natural world. In this article, we will examine the impact that organic farming has on the surrounding environment and compare it to the impact that conventional agriculture has.
The Benefits of Organic Farming:
Organic farming is based on the principles of sustainability, biodiversity, and ecological harmony. These practices seek to minimize the impact of agriculture on the environment, by promoting natural cycles and reducing the use of synthetic inputs.
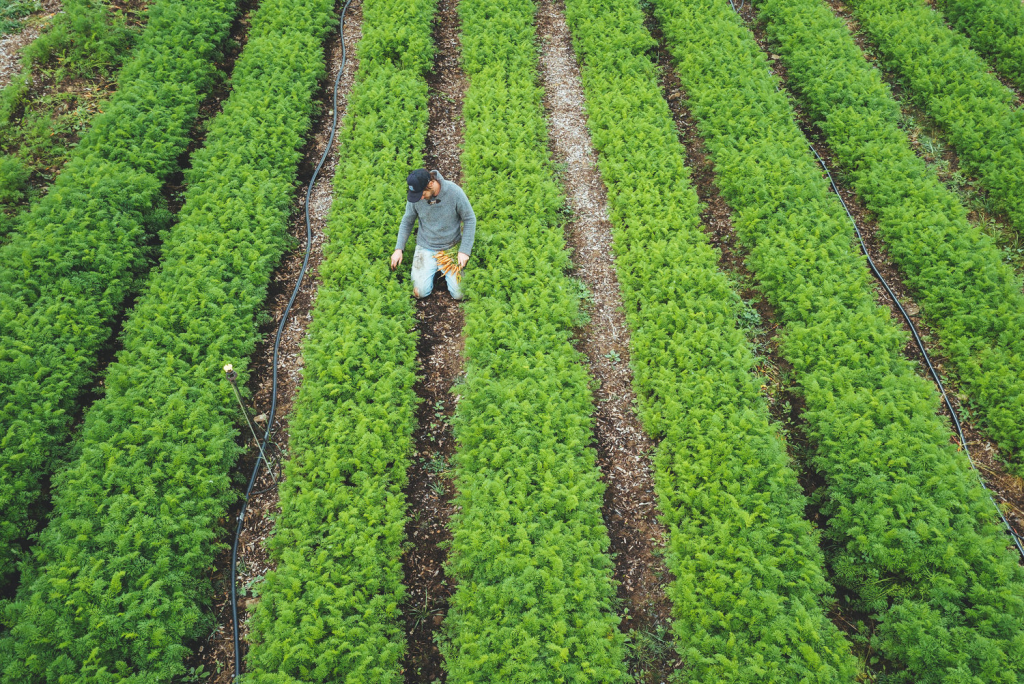

One of the most significant benefits of organic farming is its positive impact on soil health. Organic farming techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and the use of compost and manure help to maintain soil fertility and structure, reducing erosion and soil compaction. Healthy soil is critical to the long-term sustainability of agriculture and helps to reduce the environmental impact of farming.
Organic farming also reduces the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which are major contributors to water pollution and habitat destruction. By relying on natural inputs such as compost, green manure, and natural pest control, organic farming helps to reduce the release of harmful chemicals into the environment.
Comparing Organic Farming to Conventional Agriculture:
When comparing the environmental impact of organic farming to conventional agriculture, there are several key areas to consider. These include greenhouse gas emissions, water use, soil health, and biodiversity.
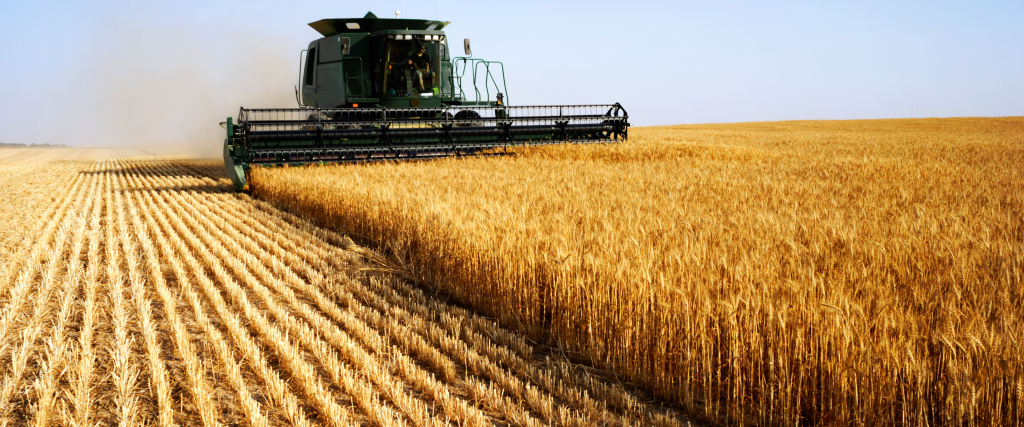
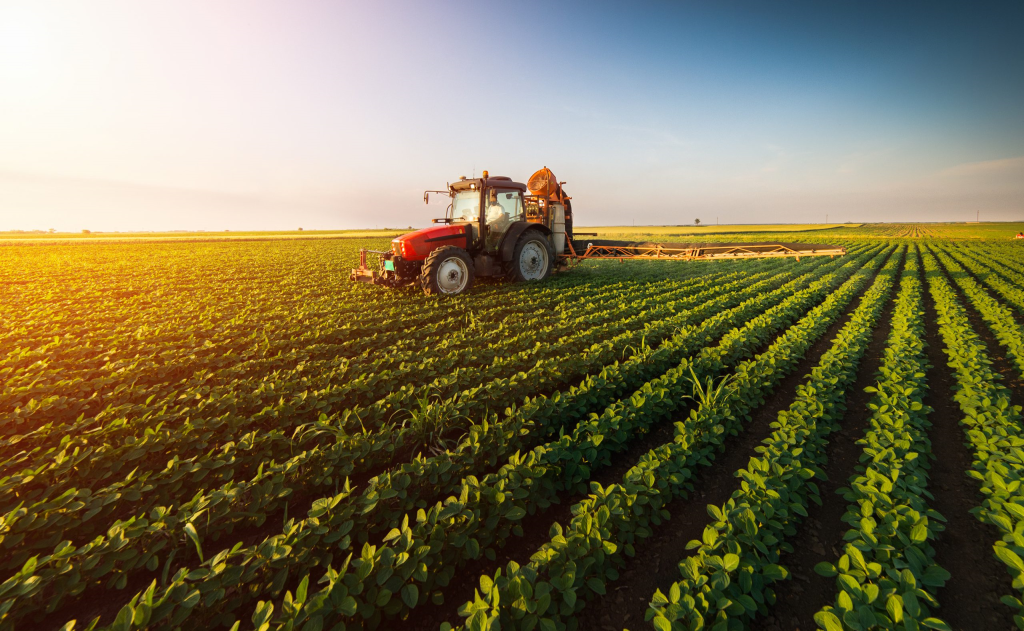


Water Use:
Organic farming uses less water than conventional agriculture, due to the use of natural methods such as crop rotation and mulching. These practices help to retain moisture in the soil, reducing the need for irrigation. In addition, organic farming does not rely on synthetic fertilizers, which can leach into waterways and cause pollution.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Organic farming has been shown to have a lower carbon footprint than conventional agriculture. Organic farming practices help to sequester carbon in the soil, reducing the amount of carbon dioxide that is released into the atmosphere. In addition, organic farming reduces the use of fossil fuels, which are a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
Soil Health:
Organic farming is known to improve soil health, which in turn has a positive impact on the environment. Healthy soil helps to retain moisture and nutrients, reducing the need for synthetic inputs. In addition, healthy soil helps to prevent erosion and improve water quality.

Biodiversity:
Organic farming is based on the principles of biodiversity, which helps to promote healthy ecosystems. Organic farms typically have a greater variety of plant and animal species, which helps to support a diverse range of habitats and promotes pollination and natural pest control.
As more and more studies demonstrate the advantages of sustainable agriculture, the positive effects that organic farming has on the surrounding ecosystem are coming into sharper focus. Organic farming can help reduce the negative effects that agriculture has on the surrounding environment because it minimizes the use of artificial inputs, prioritizes maintaining healthy soil, and encourages biodiversity. Even though there is still more work to be done to advance sustainable agriculture, organic farming presents a positive and encouraging path toward a more sustainable future.






No comment